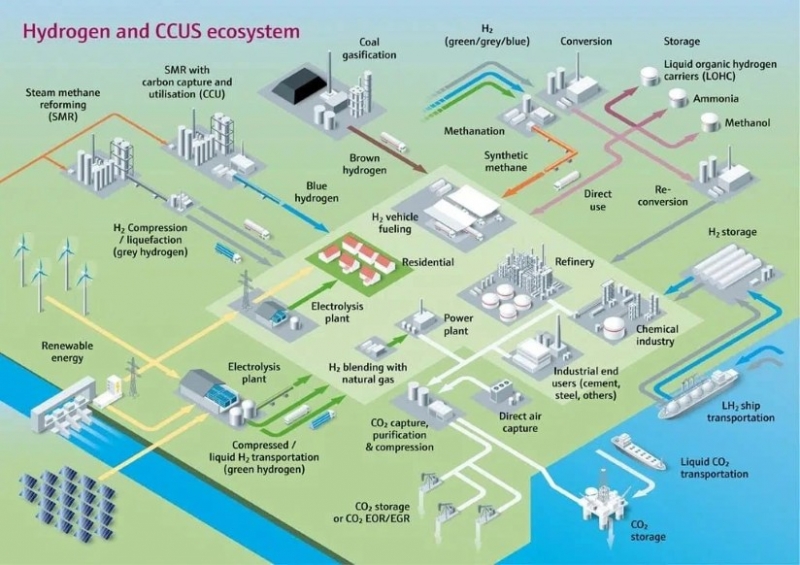
This comprehensive infographic maps out the interconnected processes of hydrogen production, conversion, transportation, storage, and utilization, alongside carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS).
Hydrogen Production Pathways
- Green Hydrogen: Produced via electrolysis powered by renewable sources (solar, wind, hydro).
- Grey Hydrogen: Generated from steam methane reforming (SMR) without carbon capture.
- Blue Hydrogen: SMR with integrated carbon capture and utilization (CCU).
- Brown Hydrogen: Derived from coal gasification.
Hydrogen Conversion & Storage
- Compression & Liquefaction: For pipeline or ship transport.
- Methanation: Converts hydrogen into synthetic methane.
- LOHCs (Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers): Enable safe storage and reconversion.
- Ammonia & Methanol: Serve as hydrogen carriers and industrial feedstocks.
Transportation Infrastructure
- Pipelines: For gaseous hydrogen and CO₂.
- Ships: Transport liquid hydrogen and CO₂.
- Trucks & Rail: For compressed or liquefied hydrogen.
End-Use Sectors
- Mobility: Fueling stations for vehicles.
- Residential & Power: Heating and electricity generation.
- Industrial: Cement, steel, refining, and chemicals.
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCUS)
- CO₂ Sources: Industrial emissions and direct air capture.
- Processing: Purification and compression.
- Storage: Geological formations or utilization in products.
This ecosystem visualizes the full lifecycle of hydrogen and CO₂, emphasizing the integration of low-carbon technologies across sectors.
平台声明:该文观点仅代表作者本人,零碳未来网 系信息发布平台,我们仅提供信息存储空间服务。







发表评论 取消回复