Hydrogenis emerging as a game-changer in the global shift toward sustainable energy. As a clean, versatile fuel, it can be produced from renewable sources and used across various industries, including transportation, power generation, and manufacturing.hashtag#Greenhydrogen, derived from waterhashtag#electrolysisusing renewable energy, offers a zero-emission solution to reduce carbon footprints and enhance energy security.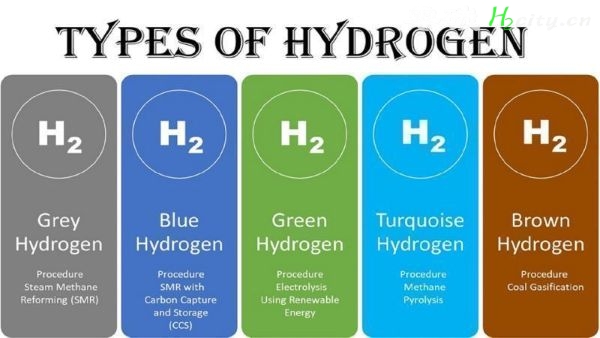
The hydrogen market is gaining strong momentum as industries and governments push toward low-carbon energy systems and long-term decarbonization goals. Hydrogen is increasingly viewed as a versatile energy carrier that can support clean power generation, industrial heat, and low-emission transportation. Technological advances in electrolysis, fuel cell efficiency, and storage solutions are improving the feasibility of green and blue hydrogen, while supportive policies, subsidies, and national hydrogen roadmaps are accelerating project development across regions.
the hydrogen market is evolving from pilot projects to integrated value chains, linking production, storage, distribution, and end-use applications. Heavy industries such as steel, chemicals, and refining are exploring hydrogen to replace fossil-based feedstocks, while mobility applications are expanding in fuel cell vehicles, rail, and maritime transport
Types of hydrogen
Hydrogen is classified into different types based on its production method and environmental impact. The most common types include:Green Hydroegn– Produced using renewable energy (like solar or wind) through electrolysis, making it the most sustainable and eco-friendly form.
Blue Hydroegn– Generated from natural gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS) to reduce emissions.
Grey Hydrogen– Derived from natural gas or fossil fuels without carbon capture, resulting in high CO₂ emissions.
Brown or Black Hydrogen– Produced from coal through gasification, emitting large amounts of CO₂.
Pink Hydrogen– Created using nuclear-powered electrolysis, offering a low-carbon alternative.
Turquoise Hydrogen – Made via methane pyrolysis, producing solid carbon instead of CO₂ emissions.
With ongoing advancements and increasing investments, hydrogen is set to play a crucial role in the future of clean energy and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The rising energy demand will drive a significant increase in oil consumption, leading to expanded production in refineries worldwide.
平台声明:该文观点仅代表作者本人,零碳未来网 系信息发布平台,我们仅提供信息存储空间服务。







发表评论 取消回复